Saturday, September 10, 2011
Pieces of the Human Evolutionary Puzzle: Who Was Australopithecus sediba?
Friday, September 9, 2011
এক ধানগাছে বারবার ধান...
 |
| নিজের উৎপাদিত ধানক্ষেতে সামনে ডঃ আবেদ চৌধুরী |
সে অতি প্রাচীনকালের কথা। তখন বঙ্গীয় বদ্বীপ অঞ্চলের বসতি স্থাপনকারীরা মাছ আর পশুপাখি শিকার করে জীবিকা নির্বাহ করত। শিকারের কাজে নদীর তীরে গেলে তারা একধরনের ঘাসজাতীয় উদ্ভিদের দেখা পেল। আগ্রহ নিয়ে কাছে যেতেই ওই ঘাসের গায়ে খুঁজে পেয়েছিল একধরনের দানাদার শস্য। সবুজ শস্য পেকে হলুদ হলে তারা গাছসহ তা কেটে বাড়িতে নিয়ে এল। খোসা ছাড়ানো ধান সেদ্ধ করে খেতে শুরু করল তারা। এভাবে শুরু হলো ধান চাষ, বর্ধিত হতে লাগল জনপদ, সভ্যতা, নগর আর রাষ্ট্র।
কালপরিক্রমায় ধান হয়ে উঠল আমাদের প্রধান খাবার।
দানাদার এই শস্যটি পেকে উঠলেই কৃষক গাছসহ তা কেটে উঠানে নিয়ে আসে। এবং ধরেই নেওয়া হলো আম-কাঁঠালের মতো বছরের পর বছর টিকে থাকার সৌভাগ্য ধানগাছের হবে না। ধানবিজ্ঞানী আবেদ চৌধুরী এটা কোনোভাবেই মানতে পারছিলেন না। ওরিজা সেটিভ নামের এই ঘাসজাতীয় গাছে ধানের দ্বিতীয় জন্ম নিয়ে তিনি বছরের পর বছর পরীক্ষা-নিরীক্ষা চালিয়ে যেতে লাগলেন। একসময় এল সফলতা। বাংলাদেশের মাটিতেই উদ্ভাবিত হলো বিশ্বের প্রথম জীবনবর্ধিত ধানের জাত। সংক্ষেপে আবেদ চৌধুরী এর নাম দিয়েছেন জীবধা।
চার বছরের গবেষণায় আবেদ চৌধুরী একফসলি হিসেবে পরিচিত ধানগাছকে দোফসলিতে পরিণত করলেন। বোরো ও আউশ মৌসুমের জন্য এমন চারটি নতুন ধানের জাত উদ্ভাবন করলেন, যা কমপক্ষে দুবার ফলন দেবে। বাংলাদেশের মৌলভীবাজার জেলার কুলাউড়া উপজেলার কানিহাটি গ্রামে নতুন এই জাতের ধান চাষ এরই মধ্যে শুরু হয়েছে। জীবধা এখন অন্যান্য অঞ্চলের কৃষকও চাষ শুরু করেছেন।
মৌলভীবাজারের ছেলে আবেদ চৌধুরী যুক্তরাষ্ট্রে কৃষি বিষয়ে উচ্চশিক্ষার লক্ষ্যে চাকরি নিয়ে পাড়ি জমিয়েছিলেন দ্বীপ মহাদেশ অস্ট্রেলিয়ায়। সেখানকার জাতীয় গবেষণা সংস্থায় ধানের জিন নিয়ে গবেষণা করে কাটিয়ে দিয়েছেন জীবনের ২০টি বছর। সার ছাড়া ধানের চারা তৈরি থেকে শুরু করে উন্নত জাতের ধান উদ্ভাবন করেছেন তিনি। পেশাগত কারণে বিদেশের মাটিতে গবেষণা করলেও দেশ নিয়ে তাঁর চিন্তা ছিল ভিন্ন। গ্রামের বাড়ি মৌলভীবাজারের কানিহাটিতে নিজের হাতে গড়ে তুলেছেন খামার। খড় বা নাড়া থেকে কৃষকদের ধান সংগ্রহ করার পদ্ধতি তাঁকে ভাবিয়ে তোলে। কিছু খড় থেকে কয়েক মাস পর যদি ধান পাওয়া যায়, তাহলে ধানগাছ জমিতে রেখে যত্ন নিলে কেন তা হবে না—এই প্রশ্ন জাগে তাঁর মনে।
দ্বিতীয় জন্মের রহস্য
আবেদ চৌধুরী খেয়াল করেন, একটি ধানগাছ পরিণত হওয়ার পর তা থেকে ৬৫টি শিষ বের হয়। এর মধ্যে ৪০টি শক্তিশালী ছড়া বের হয়, বাকিগুলো বের হতে পারে না। গোড়াসহ গাছ কেটে ফেললে বের না হওয়া ছড়াগুলো আর কখনো আলোর মুখ দেখে না। ৩৫ সেন্টিমিটার ওপর থেকে ধান কেটে নিয়ে সঠিক পরিচর্যা করলে আলোর মুখ না দেখা ২৫টি ছড়া আলোর মুখ দেখতে পারে। একবার ধান কাটার পর ইউরিয়া সার দিলে ৫০ থেকে ৫৫ দিনের মধ্যে গাছ থেকে ধান বের হয়।
আবেদ চৌধুরী তাঁর কাছে সংরক্ষিত চীন, ফিলিপাইনসহ বিশ্বের বিভিন্ন দেশ থেকে আনা ধানের জাত কানিহাটিতে চাষ শুরু করলেন। যে জাতগুলোর ধান পাকার পর কেটে নিয়ে গেলে আবার ধানের শিষ বের হয়, সেগুলো আলাদা করলেন। এভাবে তিন থেকে চারটি জাত বের করলেন তিনি। তিন বছর ধরে এই জাতগুলো চাষ করে দেখলেন, নিয়মিতভাবে এগুলো দ্বিতীয়বার ফলন দিচ্ছে।
যেসব উঁচু জমিতে বছরে একবারের বেশি ফসল হয় না, সেখানে জীবধা চাষ করা অনেক লাভজনক। প্রথমবার এক বিঘা জমিতে চাষ করতে দুই থেকে আড়াই হাজার টাকা খরচ পড়ে। পাকা ধান আগা থেকে কেটে নেওয়ার পর ওই জমিতে ৩০০ টাকার ইউরিয়া সার ছিটাতে হয়। ৫০ থেকে ৫৫ দিন পর আবারও ওই গাছে ধান ধরে।
গত দুই বছরে চাষের অভিজ্ঞতায় দেখা গেছে, নতুন এই জাত চাষ করলে প্রথমবারের তুলনায় দ্বিতীয়বার অর্ধেক পরিমাণে ধান হয়। উঁচু জমিতে এই জাতের ফলন ভালো হয়। তিন বছর ধরে কানিহাটি গ্রামে চার একর জমিতে এই জাতের চাষ করে সফলতা পাওয়া গেছে।
কৃষি মন্ত্রণালয়ের হিসাবে, দেশের ২৮ লাখ একর জমি একফসলি। এর মধ্যে প্রায় ১০ লাখ একর উঁচু জমিতে এই জাতের চাষ সম্ভব। এতে বছরে ২০ থেকে ৩০ লাখ টন অতিরিক্ত ফসল উৎপাদন করা সম্ভব। গড় উৎপাদন খরচ আগের চেয়ে অর্ধেকে নেমে আসবে।
কৃষকের জ্ঞান এগিয়েছে বিজ্ঞানীর হাত ধরে
আবেদ চৌধুরী এ ব্যাপারে বলেন, অনেক আগে থেকে কৃষক নাড়া বা খড় থেকে ধান সংগ্রহ করত। কিন্তু তা সব ধান থেকে এবং সব সময় পাওয়া যেত না। যা পাওয়া যেত, তা খুবই সামান্য। নতুন এই জাত থেকে নিশ্চিতভাবে প্রথমবারের চেয়ে অর্ধেক পরিমাণ ধান পাওয়া যাবে।
কোনো একটি জমি যতবার চাষ দেওয়া হবে, ততবার মিথেন গ্যাস ও কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড নির্গত হবে। একবার চাষ দিয়ে দুবার ফসল উৎপাদন করলে উৎপাদন খরচ কমে যাওয়ার পাশাপাশি তা কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড নিঃসরণ কমিয়ে এনে জলবায়ু পরিবর্তনে ভূমিকা রাখবে। জানান আবেদ চৌধুরী।
আবেদ চৌধুরী গত বোরো মৌসুমে কানিহাটি গ্রামের একটি ২৫ বর্গমিটারের প্রদর্শনীখেতে বোরো ধানের চারা রোপণ করেছিলেন। এ খেতে সাধারণভাবে পরিমাণমতো ইউরিয়া সার প্রয়োগ করা হয়। সঠিকভাবে সেচ ও পরিচর্যা করে ১৩০ দিনের মধ্যে ৮৫ সেন্টিমিটার থেকে এক মিটার উচ্চতার গাছে প্রথমবারের মতো ধান বেরিয়ে আসে। আর এই ১৩০ দিনের মধ্যেই মাটি থেকে ৩৫ সেন্টিমিটার উচ্চতায় পরিকল্পিতভাবে ধান কেটে নিতে হয়েছে। প্রথমবারের কেটে নেওয়া ধানখেতে নতুন করে কোনো প্রকার চাষ ছাড়াই শুধু হালকাভাবে ইউরিয়া সার প্রয়োগ করে মাত্র ৫২ দিনের মাথায় দ্বিতীয়বারের মতো ব্যাপক ফসল উৎপাদিত হয়।
প্রথমবারের নতুন ধান কেটে নেওয়ার পর হিসাব করে দেখা যায়, হেক্টরপ্রতি এ ধান উৎপাদন হয়েছে ৬ দশমিক ৪ মেট্রিক টন। প্রথমবারের ফসল কেটে নেওয়ার পর প্রতি হেক্টরে ধান উৎপাদিত হয় তিন মেট্রিক টন। একই ধানগাছ থেকে তৃতীয়বারের মতো ফসল হেক্টরপ্রতি প্রায় তিন মেট্রিক টন উৎপাদন হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা রয়েছে, যেখানে সরকারি হিসাব অনুযায়ী হেক্টরপ্রতি ধান উৎপাদন হয়ে থাকে তিন থেকে চার মেট্রিক টন।
জীবধা নিয়ে আবেদ চৌধুরীর পরিকল্পনা বিস্তর। তিনি এই জাতগুলোকে দেশের কৃষকদের কাছে পৌঁছে দিতে চান। জাত ভালো হলে এটা কৃষক থেকে কৃষকের হাতে পৌঁছে যাবে—এটাই তাঁর ভরসা। যেমন করে বাংলা অঞ্চলে একফসলি ধানের বিস্তার হয়েছিল, তেমনি করে জীবধাও সারা দেশে ছড়িয়ে পড়বে। সেদিন হয়তো দূরে নয়, জীবনবর্ধিত ধান (জীবধা) বাংলাদেশের সীমানা ছাড়িয়ে সারা পৃথিবীতে ছড়িয়ে পড়বে।
ড. আবেদ চৌধুরী: বংশগতিবিষয়ক বিজ্ঞান গবেষক, বিজ্ঞান লেখক। অস্ট্রেলিয়ায় যৌথ গবেষণায় একদল অস্ট্রেলীয় বিজ্ঞানীর সঙ্গে ফিস (ইন্ডিপেনডেন্ট সিড) জিন আবিষ্কার করেন। ফিস জিনের বীজ অনেকাংশে সারবিহীনভাবে উৎপাদন করা সম্ভব। বর্তমানে অস্ট্রেলিয়ায় গবেষণাকাজে নিয়োজিত আছেন।
সংগ্রহ: প্রথম আলো, ৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০১১
Thursday, September 8, 2011
Lichens Vs THe Almighty Prions
By Jennifer Frazer | July 25, 2011
If you had to choose the world’s most indestructible biological entity, it would be hard to do better than the prion. It’s the Rasputin of biology: cook them, freeze them, disinfect them, pressurize them, irradiate them, douse them with formalin or subject them to protein-cleaving proteases, and yet they live.
Well, not literally live. After all, they’re only proteins.
Prions — infectious misfolded proteins – have survived the pressure-cooker innards of autoclaves, the stout metal sterilizers that are the backbone of laboratory, hospital, and surgical sterilization. And they have survived for years in the punishing conditions of the outdoors — wind, cold, rain, snow, ice, heat, and ultraviolet radiation.
These two points should strike fear in the hearts of mammals everywhere, for prions cause incurable fatal neurodegenerative wasting diseases and dementias of the worst imaginable sort — the kind that swiftly strike down the hale and healthy in their prime.
If you are unfamiliar with prion diseases, that is only because you did not know they were caused by prions. In mammals: scrapie, chronic wasting disease, bovine spongiform encephalopathy, also known as mad cow disease. In humans: kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, a tidier name for, well, mad-cow disease.
Once symptoms appear in humans, tremors, convulsions, personality changes, hallucinations, and uncontrollable fits of laughter can precede death, usually within six months or so. Deer and elk slowly emaciate and glaze over mentally under the effects of the chronic wasting disease prion. Sheep with scrapie scrape the fleece from their presumably itchy backsides, and cattle with mad cow stumble around aggressively before succumbing.
Tuesday, September 6, 2011
Are Neanderthals the missing link between Human and Apes?!!!....
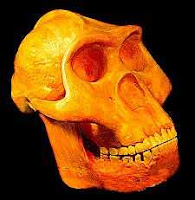 |
| Homo habilis (the first homo, 2.2-1.6 million years ago) |
Monday, September 5, 2011
ডেঙ্গু ঠেকাবে এডিস মশা!!!
Friday, September 2, 2011
Boilogical Poetry: Part 01
Thursday, September 1, 2011
Wolobachia- one Parasite to Kill all the bugs!
Wolobachia is a bacterial genus which infects arthopod species, which includes a high proportion of insect i.e. more than 60% are insects. Mosquitoes are incredibly successful parasites and cause millions of human deaths every year through the infections they spread. But they are no match for the most successful parasite of all – a bacterium called Wolbachia. It infects around 60% of the world’s insect species and it could be our newest recruit in the fight against malaria, dengue fever and other mosquito-borne infections.
Can this actually outperform that?
However, The bacterium was first identified in 1924 by Marshall Hertig and S. Burt Wolbach in Culex pipiens, a species of mosquito and Hertig formally described the genus in 1936 as Wolbachia pipientis, The parasite doesn’t generally infect Mosquitos But Scott O’Neill from the University of Queensland is leading a team of researchers who had developed a strain that not only infects mozzies, but halves the lifespans of infected females. Now, as the year comes to an end, they’re back with another piece of good news – their life-shortening bacteria also guard the mosquitoes from other infections. Infected insects are less likely to carry parasites that cause human disease, and those that do won’t live long enough to spread them. It’s a significant double-whammy that could have a lot of potential in controlling mosquito-borne diseases.
Wednesday, August 31, 2011
Epic.. Laboratory Cartoons… #Microbiology #Biotechnology
Today I am sharing some funny laboratory Cartoons… so, get ready for a ride of Humor..
The first cartoon shows what not to eat from the Microbiology-fridge..
What about lemonade from the fridge which may turn out to be a plague culture?(Left)
or fancy seeing our Microbe-Mammals created in the above Microbiology lab?(Right)
What an Eukaryote might had said after evolution to the prokaryote ancestor?(Left)
Zero Probability!!!
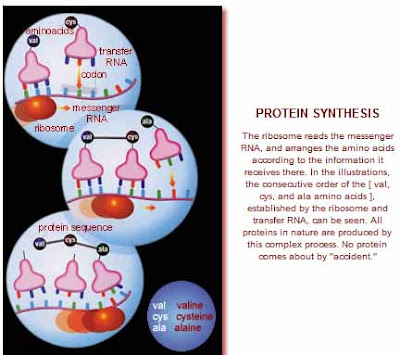 Even if we suppose that amino acids have combined and decomposed by a "trial and error" method, without losing any time since the formation of the earth, in order to form a single protein molecule, the time that would be required for something with a probability of 10950 to happen would still hugely exceed the estimated age of the earth.
Even if we suppose that amino acids have combined and decomposed by a "trial and error" method, without losing any time since the formation of the earth, in order to form a single protein molecule, the time that would be required for something with a probability of 10950 to happen would still hugely exceed the estimated age of the earth.Tuesday, August 30, 2011
Are you Confused to differentiate between “impossible” and “zero probability”?
Edward Jenner:An Inquiry into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae
 |
| Edward Jenner (1749-1823) |
Monday, August 29, 2011
A Letter of Lady Mary Montagu..
 Of the greatest diseases of mankind, small pox was one of the most feared. Not only did it kill huge numbers of people, but also survivors were scarred for life with disfiguring pockmarks. Though this disease was so harmful and dangerous, from the beginning of the eleventh century, people started to find out its solution. In 1798, Edward Jenner, found out a technique for the removal of this disease, known as Vaccination, and he became famous. But prior to the discovery of vaccination by Jenner, protection against a severe or fatal case of small pox was generally achieved by giving subjects a mild (it was hoped) case of small pox by inoculation of the small pox virus. The introduction of this operation to England is created to Lady Mary Wortley Montagu who noted that this was widely practiced in the Orient. In 1718, Lady Mary Montagu, the wife of the English Ambassador in Constantinople, decided that the technique of Variolation should be used on her children. Her own face is said to have been scarred by smallpox, so she had a special interest in the disease. However, her portrait does not show this. Her chaplain tried to dissuade her on the grounds that the technique would be ineffective in Christians. Nevertheless, Lady Mary Montagu persisted, and her children were successfully protected…
Of the greatest diseases of mankind, small pox was one of the most feared. Not only did it kill huge numbers of people, but also survivors were scarred for life with disfiguring pockmarks. Though this disease was so harmful and dangerous, from the beginning of the eleventh century, people started to find out its solution. In 1798, Edward Jenner, found out a technique for the removal of this disease, known as Vaccination, and he became famous. But prior to the discovery of vaccination by Jenner, protection against a severe or fatal case of small pox was generally achieved by giving subjects a mild (it was hoped) case of small pox by inoculation of the small pox virus. The introduction of this operation to England is created to Lady Mary Wortley Montagu who noted that this was widely practiced in the Orient. In 1718, Lady Mary Montagu, the wife of the English Ambassador in Constantinople, decided that the technique of Variolation should be used on her children. Her own face is said to have been scarred by smallpox, so she had a special interest in the disease. However, her portrait does not show this. Her chaplain tried to dissuade her on the grounds that the technique would be ineffective in Christians. Nevertheless, Lady Mary Montagu persisted, and her children were successfully protected…An interesting story about 'Miss Marry Mallon' aka 'Typhoid Marry' and 'Typhoid Fever'.
Judith Walzer Leavitt
(Between 1986 & 1906 Marry Mallon worked as a cook in 7 homes in New York city. Twenty eight cases of Typhoid Fever occured in these homes while she worked in them.
As a result the New York city health deptartment arrested Marry n admitted to an isolation hospital on North Brother island, New York.
''The world is going mad at an accelerating rate and television is the Typhoid Marry of this madness''-Edward Robb Ellis
Part of the New York American article of June 20, 1909, which first identified Mary Mallon as "Typhoid Mary" credit: New York American, June 20, 1909
Examination of Marry's stool showed that she was shedding large numbers of Typhoid bacteria (Salmonella Typhi) though she exhibited no external symptoms of the disease.An article published in 1908 in the Journal of American Medical Association referred to her as 'Typhoid Marry', an epithet by which she is still known today. She released from isolation after she pledged not to cook for others or serve food to them.Then Marry changed her name and began to work as a cook again. For 5 yrs she managed to avoid capture while continuing to spred Typhoid fever. Eventually the authorities tracked her down.She was held in custody for 23 years until she died in 1938. As a lifetime carrier,Marry Mallon was positively linked with 10 outbreaks of Typhoid Fever,53 cases and 3 deaths.(courtesy @ishzz )
Sunday, August 28, 2011
Awake …!!! What’s in your air?
Wednesday, August 24, 2011
Evolutionary synthesis: Dramatic change in our worldview
Virophage- Virus that eats virus
Viruses may cause disease but some can fall ill themselves. For the first time, a group of scientists have discovered a virus that targets other viruses. This new virus-of-viruses was discovered by Bernard La Scola and Christelle Desnues at the University of the Mediterranean, who have playfully named it Sputnik, after the Russian for "fellow traveller". It is so unique that they have classified it in an entirely new family – the "virophages" – in honour of the similarities it shares with the bacteriophage viruses that use bacteria as hosts.
fig. mavirus fig. virocapsid
The story of Sputnik started in 1992 with some dirty English water. A group of scientists were studying an amoeba taken from a cooling tower in Bradford, England, when they discovered a microscopic giant – a virus so large that it was originally mistaken for bacterium. It was only in 2003 that La Scola and colleagues conclusively showed that the new find was indeed a virus. But what a virus – APMV, or ‘mimivirus’, measures a whopping 400 nanometres across.
Thursday, August 18, 2011
The Curious case of Bdellovibrio: Beware Bacterias!
In my class 12, our teacher was teaching us bacterial taxonomy. And, he said “Beware Escherichias, we are reading Bdellovibrio.” The first impression was it was some kind of Bacteriophage, but we were damned to hear that it was actually a bacteria. While I remembered the incident, I almost forgot the name of the bacteria. It was untill yesterday, that I was reading about Virophage(sputnik.. isnt it a funny name?), I remebered what my teacher said then.
While surfing Internet I went thorough one blog, which read, “A mild ocean breeze plays over the water surface, dispelling any notion that danger lurks in the murky depths. However, a gruesome event is about to occur as a silent attacker speeds forth toward an unsuspecting victim. In a furious collision, the savage meets its target and whittles its way into the body of the innocent prey. Once inside, the transformation begins - the predator ceases its frenzy and prepares to multiply. The host is reduced to a protective cocoon, supplying food and shelter for the growing parasite. Within hours, the nourishment is drained and the ghost-like shell of the host bursts open to release a new generation of deadly predators. And all the while, the waters remain still...’’
This, actually summarizes what Bdellovibrio actually is. The Bdellovibrio (which literally means "curved leech") make a living by attacking and devouring other bacteria, and are found in diverse environments such as marine and fresh waters, sewage, and soil. The predatory bacterium Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus eats its prey-larger bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, from the inside, an example of the imaginative lengths to which some prokaryotes will go to make a living. Discovered in 1962, their lifestyle has made them hard to follow with conventional tools. It has typically two phases in its lifecycle, Attack phase and Growth Phase.



