BioGenEra
We read, we write!
Saturday, September 10, 2011
Pieces of the Human Evolutionary Puzzle: Who Was Australopithecus sediba?
Friday, September 9, 2011
এক ধানগাছে বারবার ধান...
 |
| নিজের উৎপাদিত ধানক্ষেতে সামনে ডঃ আবেদ চৌধুরী |
সে অতি প্রাচীনকালের কথা। তখন বঙ্গীয় বদ্বীপ অঞ্চলের বসতি স্থাপনকারীরা মাছ আর পশুপাখি শিকার করে জীবিকা নির্বাহ করত। শিকারের কাজে নদীর তীরে গেলে তারা একধরনের ঘাসজাতীয় উদ্ভিদের দেখা পেল। আগ্রহ নিয়ে কাছে যেতেই ওই ঘাসের গায়ে খুঁজে পেয়েছিল একধরনের দানাদার শস্য। সবুজ শস্য পেকে হলুদ হলে তারা গাছসহ তা কেটে বাড়িতে নিয়ে এল। খোসা ছাড়ানো ধান সেদ্ধ করে খেতে শুরু করল তারা। এভাবে শুরু হলো ধান চাষ, বর্ধিত হতে লাগল জনপদ, সভ্যতা, নগর আর রাষ্ট্র।
কালপরিক্রমায় ধান হয়ে উঠল আমাদের প্রধান খাবার।
দানাদার এই শস্যটি পেকে উঠলেই কৃষক গাছসহ তা কেটে উঠানে নিয়ে আসে। এবং ধরেই নেওয়া হলো আম-কাঁঠালের মতো বছরের পর বছর টিকে থাকার সৌভাগ্য ধানগাছের হবে না। ধানবিজ্ঞানী আবেদ চৌধুরী এটা কোনোভাবেই মানতে পারছিলেন না। ওরিজা সেটিভ নামের এই ঘাসজাতীয় গাছে ধানের দ্বিতীয় জন্ম নিয়ে তিনি বছরের পর বছর পরীক্ষা-নিরীক্ষা চালিয়ে যেতে লাগলেন। একসময় এল সফলতা। বাংলাদেশের মাটিতেই উদ্ভাবিত হলো বিশ্বের প্রথম জীবনবর্ধিত ধানের জাত। সংক্ষেপে আবেদ চৌধুরী এর নাম দিয়েছেন জীবধা।
চার বছরের গবেষণায় আবেদ চৌধুরী একফসলি হিসেবে পরিচিত ধানগাছকে দোফসলিতে পরিণত করলেন। বোরো ও আউশ মৌসুমের জন্য এমন চারটি নতুন ধানের জাত উদ্ভাবন করলেন, যা কমপক্ষে দুবার ফলন দেবে। বাংলাদেশের মৌলভীবাজার জেলার কুলাউড়া উপজেলার কানিহাটি গ্রামে নতুন এই জাতের ধান চাষ এরই মধ্যে শুরু হয়েছে। জীবধা এখন অন্যান্য অঞ্চলের কৃষকও চাষ শুরু করেছেন।
মৌলভীবাজারের ছেলে আবেদ চৌধুরী যুক্তরাষ্ট্রে কৃষি বিষয়ে উচ্চশিক্ষার লক্ষ্যে চাকরি নিয়ে পাড়ি জমিয়েছিলেন দ্বীপ মহাদেশ অস্ট্রেলিয়ায়। সেখানকার জাতীয় গবেষণা সংস্থায় ধানের জিন নিয়ে গবেষণা করে কাটিয়ে দিয়েছেন জীবনের ২০টি বছর। সার ছাড়া ধানের চারা তৈরি থেকে শুরু করে উন্নত জাতের ধান উদ্ভাবন করেছেন তিনি। পেশাগত কারণে বিদেশের মাটিতে গবেষণা করলেও দেশ নিয়ে তাঁর চিন্তা ছিল ভিন্ন। গ্রামের বাড়ি মৌলভীবাজারের কানিহাটিতে নিজের হাতে গড়ে তুলেছেন খামার। খড় বা নাড়া থেকে কৃষকদের ধান সংগ্রহ করার পদ্ধতি তাঁকে ভাবিয়ে তোলে। কিছু খড় থেকে কয়েক মাস পর যদি ধান পাওয়া যায়, তাহলে ধানগাছ জমিতে রেখে যত্ন নিলে কেন তা হবে না—এই প্রশ্ন জাগে তাঁর মনে।
দ্বিতীয় জন্মের রহস্য
আবেদ চৌধুরী খেয়াল করেন, একটি ধানগাছ পরিণত হওয়ার পর তা থেকে ৬৫টি শিষ বের হয়। এর মধ্যে ৪০টি শক্তিশালী ছড়া বের হয়, বাকিগুলো বের হতে পারে না। গোড়াসহ গাছ কেটে ফেললে বের না হওয়া ছড়াগুলো আর কখনো আলোর মুখ দেখে না। ৩৫ সেন্টিমিটার ওপর থেকে ধান কেটে নিয়ে সঠিক পরিচর্যা করলে আলোর মুখ না দেখা ২৫টি ছড়া আলোর মুখ দেখতে পারে। একবার ধান কাটার পর ইউরিয়া সার দিলে ৫০ থেকে ৫৫ দিনের মধ্যে গাছ থেকে ধান বের হয়।
আবেদ চৌধুরী তাঁর কাছে সংরক্ষিত চীন, ফিলিপাইনসহ বিশ্বের বিভিন্ন দেশ থেকে আনা ধানের জাত কানিহাটিতে চাষ শুরু করলেন। যে জাতগুলোর ধান পাকার পর কেটে নিয়ে গেলে আবার ধানের শিষ বের হয়, সেগুলো আলাদা করলেন। এভাবে তিন থেকে চারটি জাত বের করলেন তিনি। তিন বছর ধরে এই জাতগুলো চাষ করে দেখলেন, নিয়মিতভাবে এগুলো দ্বিতীয়বার ফলন দিচ্ছে।
যেসব উঁচু জমিতে বছরে একবারের বেশি ফসল হয় না, সেখানে জীবধা চাষ করা অনেক লাভজনক। প্রথমবার এক বিঘা জমিতে চাষ করতে দুই থেকে আড়াই হাজার টাকা খরচ পড়ে। পাকা ধান আগা থেকে কেটে নেওয়ার পর ওই জমিতে ৩০০ টাকার ইউরিয়া সার ছিটাতে হয়। ৫০ থেকে ৫৫ দিন পর আবারও ওই গাছে ধান ধরে।
গত দুই বছরে চাষের অভিজ্ঞতায় দেখা গেছে, নতুন এই জাত চাষ করলে প্রথমবারের তুলনায় দ্বিতীয়বার অর্ধেক পরিমাণে ধান হয়। উঁচু জমিতে এই জাতের ফলন ভালো হয়। তিন বছর ধরে কানিহাটি গ্রামে চার একর জমিতে এই জাতের চাষ করে সফলতা পাওয়া গেছে।
কৃষি মন্ত্রণালয়ের হিসাবে, দেশের ২৮ লাখ একর জমি একফসলি। এর মধ্যে প্রায় ১০ লাখ একর উঁচু জমিতে এই জাতের চাষ সম্ভব। এতে বছরে ২০ থেকে ৩০ লাখ টন অতিরিক্ত ফসল উৎপাদন করা সম্ভব। গড় উৎপাদন খরচ আগের চেয়ে অর্ধেকে নেমে আসবে।
কৃষকের জ্ঞান এগিয়েছে বিজ্ঞানীর হাত ধরে
আবেদ চৌধুরী এ ব্যাপারে বলেন, অনেক আগে থেকে কৃষক নাড়া বা খড় থেকে ধান সংগ্রহ করত। কিন্তু তা সব ধান থেকে এবং সব সময় পাওয়া যেত না। যা পাওয়া যেত, তা খুবই সামান্য। নতুন এই জাত থেকে নিশ্চিতভাবে প্রথমবারের চেয়ে অর্ধেক পরিমাণ ধান পাওয়া যাবে।
কোনো একটি জমি যতবার চাষ দেওয়া হবে, ততবার মিথেন গ্যাস ও কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড নির্গত হবে। একবার চাষ দিয়ে দুবার ফসল উৎপাদন করলে উৎপাদন খরচ কমে যাওয়ার পাশাপাশি তা কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড নিঃসরণ কমিয়ে এনে জলবায়ু পরিবর্তনে ভূমিকা রাখবে। জানান আবেদ চৌধুরী।
আবেদ চৌধুরী গত বোরো মৌসুমে কানিহাটি গ্রামের একটি ২৫ বর্গমিটারের প্রদর্শনীখেতে বোরো ধানের চারা রোপণ করেছিলেন। এ খেতে সাধারণভাবে পরিমাণমতো ইউরিয়া সার প্রয়োগ করা হয়। সঠিকভাবে সেচ ও পরিচর্যা করে ১৩০ দিনের মধ্যে ৮৫ সেন্টিমিটার থেকে এক মিটার উচ্চতার গাছে প্রথমবারের মতো ধান বেরিয়ে আসে। আর এই ১৩০ দিনের মধ্যেই মাটি থেকে ৩৫ সেন্টিমিটার উচ্চতায় পরিকল্পিতভাবে ধান কেটে নিতে হয়েছে। প্রথমবারের কেটে নেওয়া ধানখেতে নতুন করে কোনো প্রকার চাষ ছাড়াই শুধু হালকাভাবে ইউরিয়া সার প্রয়োগ করে মাত্র ৫২ দিনের মাথায় দ্বিতীয়বারের মতো ব্যাপক ফসল উৎপাদিত হয়।
প্রথমবারের নতুন ধান কেটে নেওয়ার পর হিসাব করে দেখা যায়, হেক্টরপ্রতি এ ধান উৎপাদন হয়েছে ৬ দশমিক ৪ মেট্রিক টন। প্রথমবারের ফসল কেটে নেওয়ার পর প্রতি হেক্টরে ধান উৎপাদিত হয় তিন মেট্রিক টন। একই ধানগাছ থেকে তৃতীয়বারের মতো ফসল হেক্টরপ্রতি প্রায় তিন মেট্রিক টন উৎপাদন হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা রয়েছে, যেখানে সরকারি হিসাব অনুযায়ী হেক্টরপ্রতি ধান উৎপাদন হয়ে থাকে তিন থেকে চার মেট্রিক টন।
জীবধা নিয়ে আবেদ চৌধুরীর পরিকল্পনা বিস্তর। তিনি এই জাতগুলোকে দেশের কৃষকদের কাছে পৌঁছে দিতে চান। জাত ভালো হলে এটা কৃষক থেকে কৃষকের হাতে পৌঁছে যাবে—এটাই তাঁর ভরসা। যেমন করে বাংলা অঞ্চলে একফসলি ধানের বিস্তার হয়েছিল, তেমনি করে জীবধাও সারা দেশে ছড়িয়ে পড়বে। সেদিন হয়তো দূরে নয়, জীবনবর্ধিত ধান (জীবধা) বাংলাদেশের সীমানা ছাড়িয়ে সারা পৃথিবীতে ছড়িয়ে পড়বে।
ড. আবেদ চৌধুরী: বংশগতিবিষয়ক বিজ্ঞান গবেষক, বিজ্ঞান লেখক। অস্ট্রেলিয়ায় যৌথ গবেষণায় একদল অস্ট্রেলীয় বিজ্ঞানীর সঙ্গে ফিস (ইন্ডিপেনডেন্ট সিড) জিন আবিষ্কার করেন। ফিস জিনের বীজ অনেকাংশে সারবিহীনভাবে উৎপাদন করা সম্ভব। বর্তমানে অস্ট্রেলিয়ায় গবেষণাকাজে নিয়োজিত আছেন।
সংগ্রহ: প্রথম আলো, ৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০১১
Thursday, September 8, 2011
Lichens Vs THe Almighty Prions
By Jennifer Frazer | July 25, 2011
If you had to choose the world’s most indestructible biological entity, it would be hard to do better than the prion. It’s the Rasputin of biology: cook them, freeze them, disinfect them, pressurize them, irradiate them, douse them with formalin or subject them to protein-cleaving proteases, and yet they live.
Well, not literally live. After all, they’re only proteins.
Prions — infectious misfolded proteins – have survived the pressure-cooker innards of autoclaves, the stout metal sterilizers that are the backbone of laboratory, hospital, and surgical sterilization. And they have survived for years in the punishing conditions of the outdoors — wind, cold, rain, snow, ice, heat, and ultraviolet radiation.
These two points should strike fear in the hearts of mammals everywhere, for prions cause incurable fatal neurodegenerative wasting diseases and dementias of the worst imaginable sort — the kind that swiftly strike down the hale and healthy in their prime.
If you are unfamiliar with prion diseases, that is only because you did not know they were caused by prions. In mammals: scrapie, chronic wasting disease, bovine spongiform encephalopathy, also known as mad cow disease. In humans: kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, a tidier name for, well, mad-cow disease.
Once symptoms appear in humans, tremors, convulsions, personality changes, hallucinations, and uncontrollable fits of laughter can precede death, usually within six months or so. Deer and elk slowly emaciate and glaze over mentally under the effects of the chronic wasting disease prion. Sheep with scrapie scrape the fleece from their presumably itchy backsides, and cattle with mad cow stumble around aggressively before succumbing.
Tuesday, September 6, 2011
Are Neanderthals the missing link between Human and Apes?!!!....
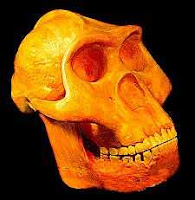 |
| Homo habilis (the first homo, 2.2-1.6 million years ago) |

